Product Description
Construction:
Fabric Carcass
Patterned Top Cover Rubber
Smooth Bottom Cover Rubber
Specifications:
0~45° inclination angle
Pattern type: V type, Cylinder type, U type
Classify by different cover rubber:
General use conveyor belt,
Oil resistant conveyor belt,
Acid/alkali resistant conveyor belt,
Heat resistant conveyor belt.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Type: | Conveyor Belt |
|---|---|
| Feature: | Wear-resistant, Heat-resistant, Tear-resistant, Flame-resistant, Cold-resistant, Acid/Alkali-Resistant |
| Usage: | Materials Handling |
| Performance: | Strong Rubber Conveyor Belt |
| Colour: | Black |
| Width: | 300~2000mm |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

What are the key differences between standard V-belts and cogged V-belts?
Standard V-belts and cogged V-belts are two variations of V-belts that differ in their design and performance characteristics. Here are the key differences between these two types of belts:
- Design:
- Flexibility:
- Heat Dissipation:
- Power Transmission Capacity:
- Noise and Vibration:
- Application Suitability:
Standard V-belts have a smooth, continuous surface on the inside, which comes in contact with the pulleys. On the other hand, cogged V-belts have notches or cogs on the inside surface. These cogs allow the belt to flex more easily and improve its flexibility and bending capabilities.
The presence of cogs in cogged V-belts makes them more flexible compared to standard V-belts. This increased flexibility allows cogged V-belts to bend and wrap around smaller pulleys more easily. It also reduces the bending stress and heat generation, resulting in improved performance and longer belt life.
Cogged V-belts have better heat dissipation properties compared to standard V-belts. The cogs create additional surface area, which improves airflow and heat dissipation during operation. This helps to reduce heat buildup and minimize the risk of belt slippage or premature wear due to excessive heat.
Standard V-belts and cogged V-belts have similar power transmission capacity for most applications. However, cogged V-belts may have a slightly reduced power capacity compared to standard V-belts due to the presence of cogs, which can reduce the contact area with the pulleys. As a result, cogged V-belts are typically used in applications that require moderate power transmission.
Cogged V-belts generally produce less noise and vibration compared to standard V-belts during operation. The presence of cogs helps to reduce the vibration and noise caused by belt slippage or engagement with the pulleys. This makes cogged V-belts suitable for applications where noise reduction is important, such as in HVAC systems or household appliances.
Standard V-belts are commonly used in a wide range of industrial applications for power transmission. They are suitable for applications with larger pulleys and higher power requirements. Cogged V-belts, on the other hand, are often preferred in applications that involve smaller pulleys, tighter spaces, or where improved flexibility and reduced noise are desired.
It’s important to consider the specific requirements of the application and consult the manufacturer’s recommendations when choosing between standard V-belts and cogged V-belts. Understanding the key differences between these two types of belts can help in selecting the most appropriate option for a particular power transmission application.
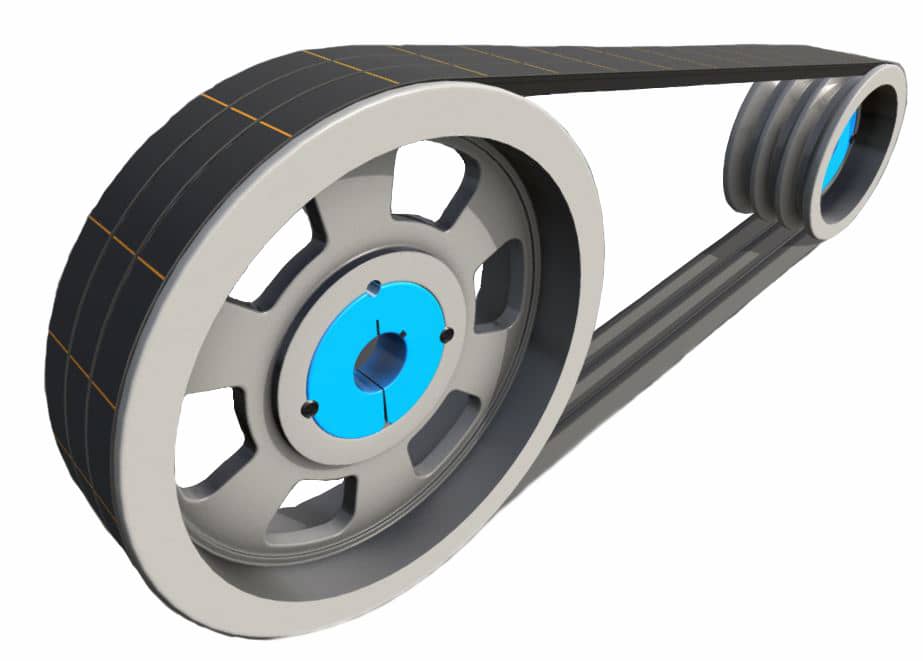
How do you troubleshoot common issues with V-belts, such as slipping or squealing?
Troubleshooting common issues with V-belts, such as slipping or squealing, is essential to maintain the proper operation and efficiency of the belt drive system. Here are some troubleshooting steps to address these issues:
- Slipping:
- Check the belt tension: Insufficient tension is a common cause of slipping. Ensure that the V-belt is properly tensioned according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. Adjust the tension by using the appropriate tensioning method or tools.
- Inspect for wear or damage: Examine the V-belt for signs of wear, cracks, fraying, or other damage. A worn-out belt may not provide adequate grip and can lead to slipping. Replace the belt if necessary.
- Check pulley alignment: Misaligned pulleys can cause the belt to slip. Verify that the pulleys are properly aligned both parallel and angularly. Adjust the pulley positions if misalignment is detected.
- Assess pulley condition: Worn or damaged pulleys can contribute to belt slipping. Inspect the pulleys for wear, rough surfaces, or damage. If needed, replace the pulleys to ensure proper belt engagement.
- Verify the load and application: Excessive loads or improper application can cause the belt to slip. Ensure that the belt drive system is designed and rated for the specific load requirements.
- Squealing:
- Check belt tension: Insufficient or excessive belt tension can lead to squealing. Adjust the tension to the recommended range specified by the manufacturer.
- Inspect for wear or contamination: Check the V-belt for signs of wear, glazing, or contamination. Worn or contaminated belts may produce squealing noises. Replace the belt if necessary and eliminate any contamination from the belt or pulleys.
- Examine pulley condition: Damaged or worn pulleys can create noise. Inspect the pulleys for wear, damage, or rough surfaces. Replace any worn or damaged pulleys.
- Verify pulley alignment: Misaligned pulleys can cause the belt to run at an angle, resulting in noise. Ensure that the pulleys are correctly aligned both parallel and angularly. Adjust the pulley positions if misalignment is detected.
- Check for belt glazing: Belt glazing occurs when the belt’s contact surface becomes smooth and glossy, reducing traction. If glazing is present, roughen the belt’s surface with fine sandpaper or replace the belt if necessary.
- Assess environmental factors: Environmental conditions, such as excessive heat or humidity, can affect belt performance. Ensure that the belt drive system operates within the recommended temperature and humidity ranges.
Slipping occurs when the V-belt fails to maintain proper traction with the pulleys, resulting in reduced power transmission and potential belt wear. To troubleshoot slipping issues:
Squealing noises from V-belts are often caused by vibrations, misalignment, or improper tension. To troubleshoot squealing issues:
By following these troubleshooting steps, you can identify and address common issues with V-belts, such as slipping or squealing. Regular maintenance, proper tensioning, and alignment are crucial for ensuring the smooth and efficient operation of the belt drive system.

What are the different types of V-belts available and their applications?
There are several types of V-belts available, each designed for specific applications and requirements. The most common types of V-belts include:
- Classic V-belts: Also known as conventional V-belts, these are the standard V-belts with a trapezoidal cross-section. They are widely used in various industrial applications for general power transmission, such as in HVAC systems, agricultural machinery, and industrial equipment.
- Narrow V-belts: Narrow V-belts are narrower than classic V-belts and have a narrower V-shaped profile. They are suitable for applications where space is limited or where high-speed ratios are required. These belts are commonly used in automotive engines, power tools, and small appliances.
- Wedge V-belts: Wedge V-belts, also known as narrow section V-belts, have a wider and deeper V-shaped cross-section compared to classic V-belts. This design allows for higher power transmission capacity and better resistance to belt slippage. Wedge V-belts are used in heavy-duty applications, such as in industrial machinery, mining equipment, and large agricultural machinery.
- Double V-belts: Double V-belts consist of two V-belts joined side by side. These belts provide increased power transmission capacity and are commonly used in applications where high torque is required, such as in heavy-duty machinery, pumps, and compressors.
- Variable Speed V-belts: Variable speed V-belts, also known as V-ribbed belts or multi-rib belts, have a ribbed surface on one side of the belt. This design allows for improved flexibility and enhanced power transmission efficiency. Variable speed V-belts are commonly used in automotive engines, industrial machinery, and appliances where variable speed control is required.
The choice of V-belt type depends on factors such as the power transmission requirements, space limitations, speed ratios, and the specific application. It is important to select the appropriate V-belt type based on these factors to ensure efficient and reliable power transmission.
In summary, the different types of V-belts available include classic V-belts, narrow V-belts, wedge V-belts, double V-belts, and variable speed V-belts. Each type has its own characteristics and is suitable for specific applications based on power transmission needs and requirements.


editor by CX 2024-04-30