Product Description
Product Description:
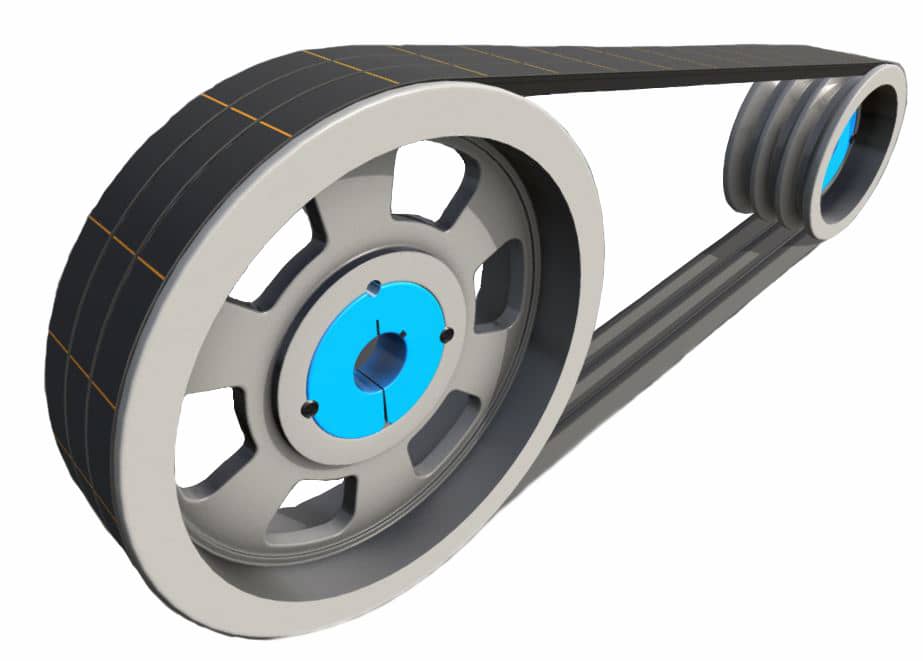
The top and the bottom are encased by the weapper, Both sides are rubber . V belt of tooth shape groove is designed for the bottom to improve the tlexral property.
- Large intensity,high flexibility,good durability
- Special Bottom rubber used,small elongation and long service life
- Excellent heat-resistance,oil-proof,and wearing resistance
- High transmission efficiency
- Suitable for band pulley with minor diameter
- Safe performance can be guaranteed even during high-speed operation
| Structure |
| No. | Name | Function | Material |
| 1 | Top Fabric | Protect the CZPT tensile member | Polyester Cotton Canvas |
| 2 | Core Cord | Nuclear material to pass the dynamic force | Polyester |
| 3 | Bottom Rubber | Side compression resistant and section | CR,EPDM |
| 4 | Bottom Fabric | Absorb the impact and prevent crack of the core rubber | Elastic Fabric |
| Section Size of lndustrial Raw Edge V Belts |
| Type | Top width (mm) | Belt Thickness (mm) | Angle(°) |
| HM | 10.5 | 8.0 | 38 |
| AX | 13 | 8.0 | 38 |
| BX | 17 | 11 | 38 |
| CX | 22 | 14 | 38 |
| DX | 32 | 19 | 38 |
| EX | 38 | 23 | 38 |
| Section Size of Raw Edge Narrow Belts |
| Type | Top width | Belt Thickness | Angle |
| XPZ | 9.7 | 8.0 | 40 |
| XPA | 12.7 | 10 | 40 |
| XPB | 16.3 | 13 | 40 |
| XPC | 22 | 18 | 40 |
| 9NX | 9.5 | 8 | 40 |
| 15NX | 16 | 13.5 | 40 |
| 25NX | 25.4 | 23 | 40 |
| Section Size of Raw Edge V Belts for Automobile |
| Type | Top width | Wrapped V belt | Raw edge V belt | REF | REC | Angle |
| AV-10/9.5 | 10.0 | 8.0 | 7.5 | 7.5 | 8.0 | 40 |
| AV-13/12.5 | 13.0 | 10.0 | 8.5 | 8.5 | 9.0 | 40 |
| AV-15 | 15.0 | 9.0 | – | – | – | 40 |
| AV-17 | 16.5 | 10.5 | 9.5 | 9.5 | 11.0 | 40 |
| AV-22 | 22.0 | 14.0 | – | – | 13.0 | 40 |
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Standard or Nonstandard: | Standard |
|---|---|
| Application: | Textile Machinery, Conveyer Equipment, Food Machinery, Agricultural Machinery |
| Feature: | Anti-Static, Oil-Resistant, Cold-Resistant, Heat-Resistant, Wear-Resistant, High Temperature-Resistance |
| Samples: |
US$ 5/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | Order Sample Support customization, please consult after order
|
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|

How do you calculate the power rating and speed capacity of a V-belt system?
Calculating the power rating and speed capacity of a V-belt system involves considering various factors such as belt type, pulley dimensions, belt tension, and speed. Here’s a general overview of the calculations involved:
- Power Rating Calculation:
- Speed Capacity Calculation:
To calculate the power rating of a V-belt system, you need to determine the maximum power that the belt can transmit without slipping or experiencing excessive wear. The power rating is typically expressed in horsepower (HP) or kilowatts (kW).
The formula for calculating the power rating is:
Power (HP or kW) = (Tension in belt (lb or N) * Belt speed (ft/min or m/s)) / 33,000 (for HP) or 1,000 (for kW)
The tension in the belt can be determined based on the design requirements of the system and is influenced by factors such as the type of application and the desired safety factor.
The speed capacity of a V-belt system is the maximum rotational speed at which the belt can operate without experiencing excessive vibration or failure. It is typically expressed in revolutions per minute (RPM).
The formula for calculating the speed capacity is:
Speed (RPM) = (Belt pitch diameter (in or mm) * π * Belt speed (ft/min or m/s)) / 12 (for in) or 1000 (for mm)
The belt pitch diameter is determined based on the pulley dimensions and is the effective diameter at which the belt engages with the pulley.
It’s important to note that these calculations provide general guidelines, and actual power rating and speed capacity may vary depending on the specific belt and pulley design, as well as other factors such as belt tensioning, environmental conditions, and system efficiency. It is recommended to consult the belt manufacturer’s guidelines or seek assistance from an engineer experienced in power transmission systems to ensure accurate calculations and appropriate belt selection for a given application.

Are there any safety considerations when working with V-belts?
Working with V-belts involves certain safety considerations to ensure the well-being of personnel and the proper functioning of the belt drive system. Here are some important safety considerations when working with V-belts:
- Lockout/Tagout: Before performing any maintenance or adjustment on a belt drive system, it is crucial to follow proper lockout/tagout procedures. Lockout/tagout involves isolating the power source, de-energizing the equipment, and securing it with locks or tags to prevent unintentional startup or release of stored energy. This ensures the safety of personnel working on or near the V-belts.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): When working with V-belts, appropriate personal protective equipment should be worn as per the specific tasks and potential hazards. This may include safety glasses, gloves, hearing protection, and protective clothing to safeguard against potential injury from flying debris, pinch points, or contact with rotating parts.
- Training and Familiarity: Ensure that personnel working with V-belts are adequately trained on safe work practices, including proper maintenance procedures, tensioning techniques, and the use of tools and equipment. Familiarity with the specific belt drive system and understanding the potential hazards associated with V-belts is essential for safe operation.
- Machine Guarding: Install appropriate machine guarding to prevent accidental contact with moving V-belts and exposed pulleys. Guards should be designed to prevent access to hazardous areas and comply with relevant safety regulations. Regularly inspect and maintain the guards to ensure their effectiveness.
- Tensioning and Adjustment: Follow proper procedures when tensioning or adjusting V-belts. Use the recommended tools and techniques specified by the manufacturer. Improper tensioning can lead to belt slippage, increased wear, and potential accidents. Avoid working near or reaching into the belt drive system while it is in operation.
- Proper Lifting and Handling: V-belts can be heavy and awkward to handle, especially in larger sizes. When lifting or handling V-belts, use proper lifting techniques and equipment to prevent strains or injuries. Avoid placing excessive stress on the belts during installation or removal.
- Maintaining Cleanliness: Keep the work area clean and free from debris, oil, or other contaminants that may affect traction or create slip hazards. Clean up any spills promptly and use appropriate cleaning methods to avoid slipping or tripping accidents.
- Manufacturer’s Guidelines: Adhere to the manufacturer’s guidelines, instructions, and specifications for the installation, tensioning, maintenance, and replacement of V-belts. Manufacturers provide valuable information on safe operating practices, recommended tension ranges, load capacities, and other relevant safety considerations specific to their V-belt products.
By following these safety considerations when working with V-belts, you can help mitigate potential hazards, reduce the risk of accidents, and ensure the safe and efficient operation of the belt drive system.
What are the different types of V-belts available and their applications?
There are several types of V-belts available, each designed for specific applications and requirements. The most common types of V-belts include:
- Classic V-belts: Also known as conventional V-belts, these are the standard V-belts with a trapezoidal cross-section. They are widely used in various industrial applications for general power transmission, such as in HVAC systems, agricultural machinery, and industrial equipment.
- Narrow V-belts: Narrow V-belts are narrower than classic V-belts and have a narrower V-shaped profile. They are suitable for applications where space is limited or where high-speed ratios are required. These belts are commonly used in automotive engines, power tools, and small appliances.
- Wedge V-belts: Wedge V-belts, also known as narrow section V-belts, have a wider and deeper V-shaped cross-section compared to classic V-belts. This design allows for higher power transmission capacity and better resistance to belt slippage. Wedge V-belts are used in heavy-duty applications, such as in industrial machinery, mining equipment, and large agricultural machinery.
- Double V-belts: Double V-belts consist of two V-belts joined side by side. These belts provide increased power transmission capacity and are commonly used in applications where high torque is required, such as in heavy-duty machinery, pumps, and compressors.
- Variable Speed V-belts: Variable speed V-belts, also known as V-ribbed belts or multi-rib belts, have a ribbed surface on one side of the belt. This design allows for improved flexibility and enhanced power transmission efficiency. Variable speed V-belts are commonly used in automotive engines, industrial machinery, and appliances where variable speed control is required.
The choice of V-belt type depends on factors such as the power transmission requirements, space limitations, speed ratios, and the specific application. It is important to select the appropriate V-belt type based on these factors to ensure efficient and reliable power transmission.
In summary, the different types of V-belts available include classic V-belts, narrow V-belts, wedge V-belts, double V-belts, and variable speed V-belts. Each type has its own characteristics and is suitable for specific applications based on power transmission needs and requirements.


editor by CX 2024-05-10